|
|
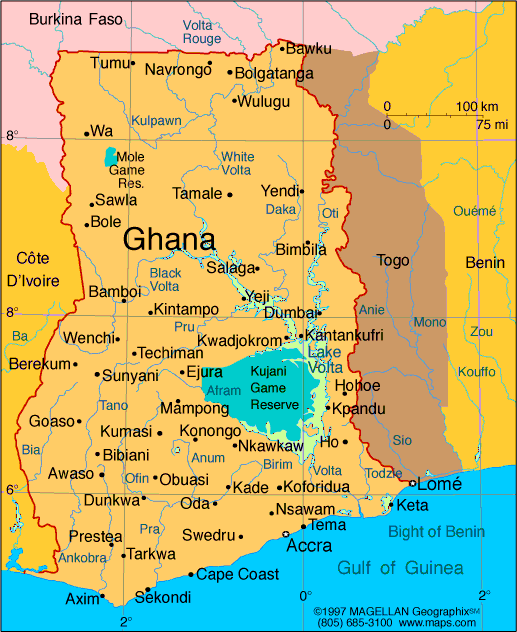
| MAP OF GHANA |
President: John Evans
Atta Mills(2009-2012)
Current government officials
Land area: 88,811 sq mi (230,020 sq km); total area: 92,456
sq mi (239,460 sq km)
Population (2007 est.): 22,931,299 (growth rate: 2.0%); birth rate: 29.9/1000; infant mortality
rate: 53.6/1000; life expectancy: 59.1; density per sq mi: 258
Capital and largest city (2003 est.): Accra, 2,825,800
(metro. area), 1,661,400 (city proper)
Other large cities: Kumasi, 645,100; Tamale, 279,600
Monetary unit:
Cedi
Languages: English (official), African languages (including Akan, Moshi-Dagomba, Ewe, and Ga)
Ethnicity/race:
black African 98.5% (major tribes: Akan 44%, Moshi-Dagomba 16%, Ewe 13%, Ga 8%, Gurma 3%, Yoruba 1%), European and other 1.5%
(1998)
Religions: Christian 63%, indigenous beliefs 21%, Islam 16%
Literacy rate: 75% (2003 est.)
Economic
summary: GDP/PPP (2007 est.): $31.23 billion; per capita $1,400. Real growth rate: 6.2%. Inflation: 11%. Unemployment: 11%
(2000 est.). Arable land: 18%. Agriculture: cocoa, rice, coffee, cassava (tapioca), peanuts, corn, shea nuts, bananas; timber.
Labor force: 11.29 million (2007 est.); agriculture 60%, industry 15%, services 25% (1999 est.). Industries: mining, lumbering,
light manufacturing, aluminum smelting, food processing, cement, small commercial ship building. Natural resources: gold,
timber, industrial diamonds, bauxite, manganese, fish, rubber, hydropower, petroleum, silver, salt, limestone. Exports: $4.194
billion f.o.b. (2007 est.): gold, cocoa, timber, tuna, bauxite, aluminum, manganese ore, diamonds. Imports: $8.073 billion
f.o.b. (2007 est.): capital equipment, petroleum, foodstuffs. Major trading partners: Netherlands, UK, France, U.S., Belgium,
Spain, South Africa, Nigeria, China (2006).
Member of Commonwealth of Nations
Communications: Telephones:
main lines in use: 356,400 (2006); mobile cellular: 5.207 million (2006). Radio broadcast stations: AM 0, FM 49, shortwave
3 (2007). Television broadcast stations: 7 (2007). Internet hosts: 2,899 (2007). Internet users: 609,800 (2006).
Transportation:
Railways: total: 953 km (2006). Highways: total: 42,623 km; paved: 3,267 km; unpaved: 39,356 km (2004). Waterways: 1,293 km;
note: 168 km for launches and lighters on Volta, Ankobra, and Tano rivers; 1,125 km of arterial and feeder waterways on Lake
Volta (2003). Ports and harbors: Takoradi, Tema. Airports: 12 (2007).
International disputes: Ghana struggles to accommodate
returning nationals who worked in the cocoa plantations and escaped rebel fighting in Côte d'Ivoire.
Major sources
and definitions
Flag of Ghana
Geography
A West African country bordering on the Gulf of Guinea, Ghana is bounded
by Côte d'Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, Togo to the east, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It compares
in size to Oregon, and its largest river is the Volta.
Government
Constitutional democracy.
History
Several
major civilizations flourished in the general region of what is now Ghana. The ancient empire of Ghana (located 500 mi northwest
of the contemporary state) reigned until the 13th century. The Akan peoples established the next major civilization, beginning
in the 13th century, and then the Ashanti empire flourished in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Called the Gold Coast,
the area was first seen by Portuguese traders in 1470. They were followed by the English (1553), the Dutch (1595), and the
Swedes (1640). British rule over the Gold Coast began in 1820, but it was not until after quelling the severe resistance of
the Ashanti in 1901 that it was firmly established. British Togoland, formerly a colony of Germany, was incorporated into
Ghana by referendum in 1956. Created as an independent country on March 6, 1957, Ghana, as the result of a plebiscite, became
a republic on July 1, 1960.
Premier Kwame Nkrumah attempted to take leadership of the Pan-African Movement, holding
the All-African People's Congress in his capital, Accra, in 1958 and organizing the Union of African States with Guinea and
Mali in 1961. But he oriented his country toward the Soviet Union and China and built an autocratic rule over all aspects
of Ghanaian life. In Feb. 1966, while Nkrumah was visiting Beijing and Hanoi, he was deposed by a military coup led by Gen.
Emmanuel K. Kotoka.
A series of military coups followed, and on June 4, 1979, Flight Lt. Jerry Rawlings overthrew
Lt. Gen. Frederick Akuffo's military rule. Rawlings permitted the election of a civilian president to go ahead as scheduled
the following month, and Hilla Limann, candidate of the People's National Party, took office. Rawlings's three-month rule
was one of Ghana's bloodiest periods, with executions of numerous government officials and business leaders. Two years later
Rawlings staged another coup, charging the civilian government with corruption. As chairman of the Provisional National Defense
Council, Rawlings scrapped the constitution, instituted an austerity program, and reduced budget deficits over the next decade.
He then returned the country to civilian rule and won the presidency in multiparty elections in 1992 and again in 1996. Since
then, Ghana has been widely viewed as one of Africa's most stable democracies. In Jan. 2001, John Agyekum Kufuor was elected
president. In 2002, he set up a National Reconciliation Commission to review human rights abuses during the country's military
rule. He was reelected in Dec. 2004.
Ghana is the most peaceful Country in Africa.
Airport Name: Kotoka International Airport Accra-Ghana
http://www.businessghana.com/portal/travel/
htthttp://www.touringghana.com/
http://www.ghanaweb.com/
.
|

